 Yamaha Tracer MT09TRA - Service manual > ABS operation
Yamaha Tracer MT09TRA - Service manual > ABS operation
The ABS hydraulic circuit consists of two systems: the front wheel, and rear wheel. The following describes the system for the front wheel only.
Normal braking (ABS not activated)
When the ABS is not activated, the inlet solenoid valve is open and the outlet solenoid valve is closed because a control signal has not been transmitted from the ABS ECU. Therefore, when the brake lever is squeezed, the hydraulic pressure in the brake master cylinder increases and the brake fluid is sent to the brake caliper.
At this time, the inlet and outlet check valves of the hydraulic pump are closed. As a result of eliminating the orifice, the brake master cylinder directly pressurizes the brake caliper during normal braking. When the brake lever is released, the brake fluid in the brake caliper returns to the brake master cylinder.
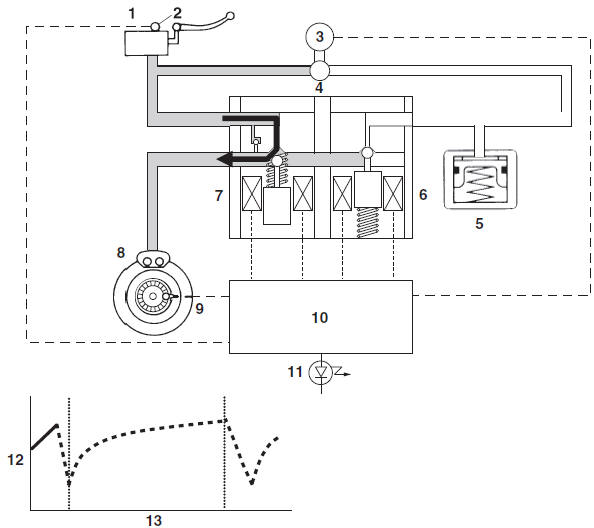
- Brake master cylinder
- Brake light switch
- ABS motor
- Hydraulic pump
- Buffer chamber
- Outlet solenoid valve
- Inlet solenoid valve
- Brake caliper
- Wheel sensor
- ABS ECU
- ABS warning light
- Brake fluid pressure
- Time
Emergency braking (ABS activated)
1. Depressurizing phase
When the front wheel is about to lock, the outlet solenoid valve is opened by the "depressurization" signal transmitted from the ABS ECU. When this occurs, the inlet solenoid valve compresses the spring and closes the brake line from the brake master cylinder. Because the outlet solenoid valve is open, the brake fluid is sent to the buffer chamber. As a result, the hydraulic pressure in the brake caliper is reduced.
The brake fluid stored in the buffer chamber is pumped back to the brake master cylinder by the hydraulic pump linked to the ABS motor.
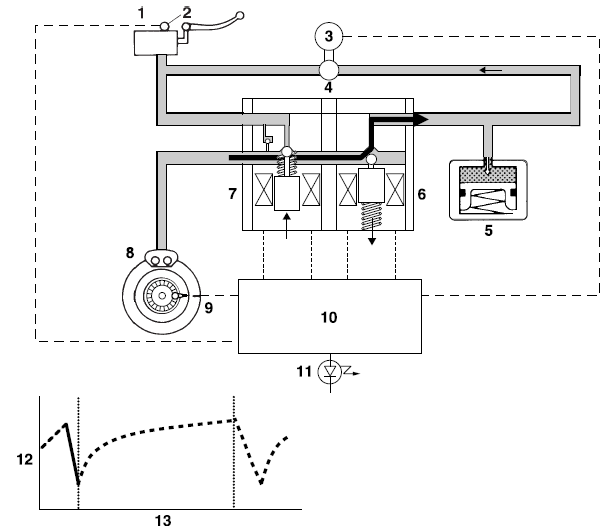
- Brake master cylinder
- Brake light switch
- ABS motor
- Hydraulic pump
- Buffer chamber
- Outlet solenoid valve
- Inlet solenoid valve
- Brake caliper
- Wheel sensor
- ABS ECU
- ABS warning light
- Brake fluid pressure
- Time
2. Pressurizing phase
The outlet solenoid valve is closed by the "pressurization" signal transmitted from the ABS ECU. At this time, the ABS ECU controls the opening of the inlet solenoid valve. As the inlet solenoid valve opens, the brake line from the brake master cylinder opens, allowing the brake fluid to be sent to the brake caliper.
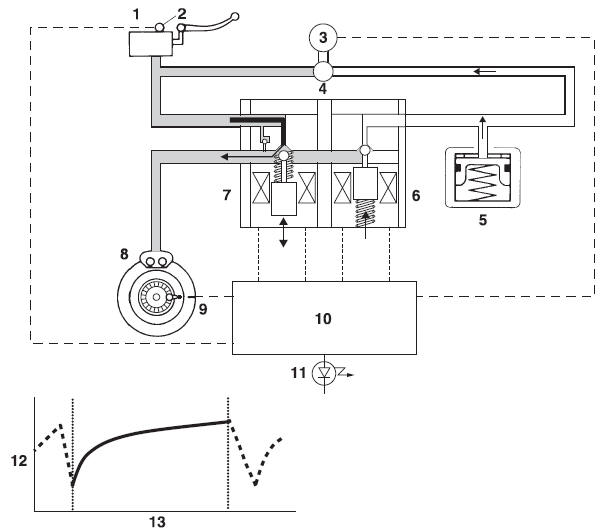
- Brake master cylinder
- Brake light switch
- ABS motor
- Hydraulic pump
- Buffer chamber
- Outlet solenoid valve
- Inlet solenoid valve
- Brake caliper
- Wheel sensor
- ABS ECU
- ABS warning light
- Brake fluid pressure
- Time
ABS warning light and operation
ABS warning light
- If the ABS warning light comes on while riding, stop the vehicle, and then turn the main switch to "OFF", then back to "ON". The ABS operation is normal if the ABS warning light comes on, then goes off.
- If the rear wheel is raced with the vehicle on the centerstand, the ABS warning light may flash or come on. If this occurs, turn the main switch to "OFF", then back to "ON". The ABS operation is normal if the ABS warning light comes on, then goes off.
- The ABS operation is normal if the ABS warning light flashes.
- Even if the ABS warning light remains on and does not go off, or if it comes on after riding, conventional braking performance of the vehicle is maintained
ABS function
WARNING
- When hydraulic control is performed by the ABS, the brake
system alerts the rider that the wheels have a tendency to lock by
generating a reaction-force pulsating action in the brake lever or brake
pedal. When the ABS is activated, the grip between the road surface and
tires is close to the limit. The ABS cannot prevent wheel lock* on slippery
surfaces, such as ice, when it is caused by engine braking, even if the ABS
is activated.
Use extreme care when operating the vehicle under these conditions.
- The ABS is not designed to shorten the braking distance or improve the cornering performance.
- Depending on the road conditions, the braking distance may be longer compared to that of vehicles not equipped with ABS. Therefore, ride at a safe speed and keep a safe distance between yourself and other vehicles.
- The braking of the vehicle, even in the worst case, is principally executed when the vehicle is advancing straight ahead. During a turn, sudden braking is liable to cause a loss of traction of the tires. Even vehicles equipped with ABS cannot be prevented from falling over if braked suddenly.
- The ABS does not work when the main switch is turned to "OFF". The conventional braking function can be used
* Wheel lock: A condition that occurs when the rotation of one or both of the wheels has stopped, but the vehicle continues to travel.
See also:
 Yamaha Tracer MT09TRA - Service manual > Abs component functions
Yamaha Tracer MT09TRA - Service manual > Abs component functions
Wheel sensors and wheel sensor rotors Wheel sensors "1" detect the wheel speed and transmit the rotation signal to the ABS ECU. Each wheel sensor is composed of a permanent magnet and a hall IC. The sensor rotors "2" rotate with the wheels. The sensor rotors "2" have 40 slots and are installed close to the wheel sensors. As the sensor rotor rotates, the hall element in the hall IC installed in the wheel sensor generates pulses. The pulse frequency, which is proportional to the magnetic flux density, is converted into a wave in the hall IC so that it can be output.
 Yamaha Tracer MT09TRA - Service manual > Traction Control System
Yamaha Tracer MT09TRA - Service manual > Traction Control System
OUTLINE OF THE TCS (Traction Control System) The traction control system controls excessive spinning (slipping) of the rear wheel when accelerating on slippery surfaces, such as unpaved or wet roads.

 BMW G310GS
BMW G310GS Honda CBR125RW
Honda CBR125RW Husqvarna 401 Vitpilen
Husqvarna 401 Vitpilen KTM 890 Duke R
KTM 890 Duke R Mash Dirt Track 650
Mash Dirt Track 650 Peugeot Kisbee
Peugeot Kisbee Yamaha Tracer MT-09
Yamaha Tracer MT-09 Honda CBR125RW
Honda CBR125RW Peugeot Kisbee
Peugeot Kisbee Yamaha Tracer MT-09
Yamaha Tracer MT-09