 Honda CBR125RW - Service manual > PGM-FI
Honda CBR125RW - Service manual > PGM-FI
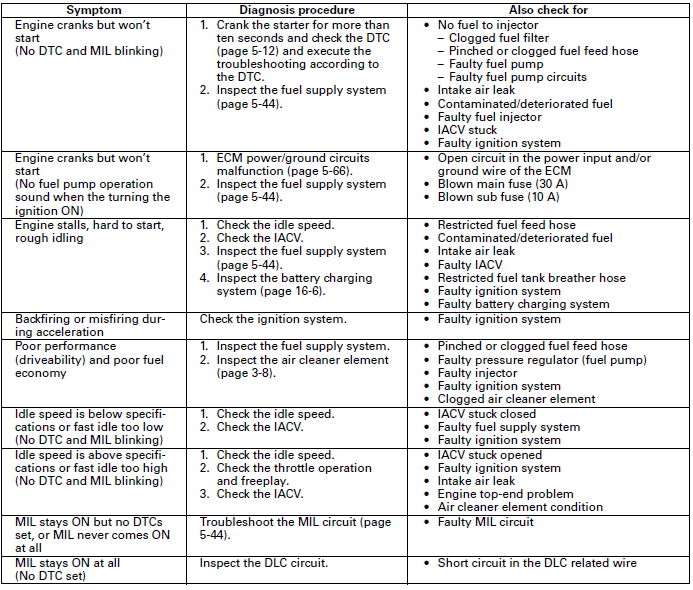
PGM-FI SYMPTOM TROUBLESHOOTING
When the motorcycle has one of these symptoms, check the DTC or MIL blinking, refer to the DTC index and begin the appropriate troubleshooting procedure. If there are no DTC/MIL blinking stored in the ECM memory, do the diagnostic procedure for the symptom, in sequence listed below, until you find cause.
PGM-FI SYSTEM LOCATION
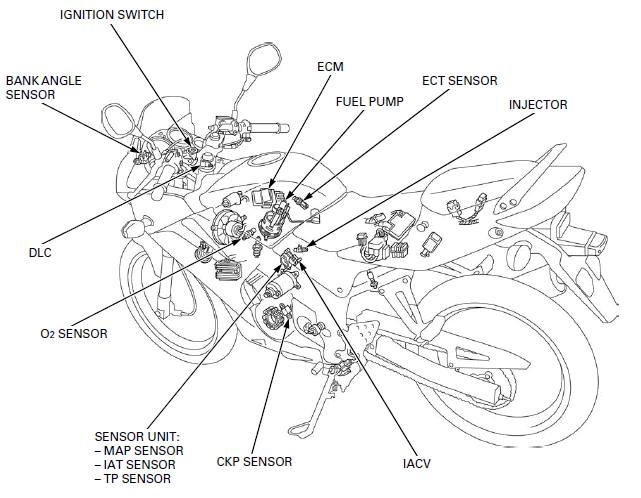
- IGNITION SWITCH
- BANK ANGLE SENSOR
- DLC
- O2 SENSOR
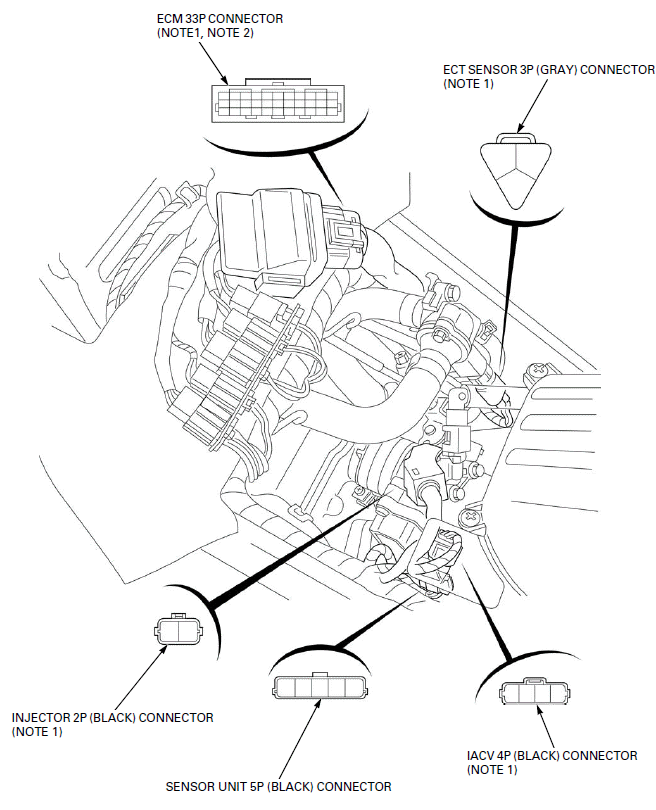
- ECM
- FUEL PUMP
- ECT SENSOR
- INJECTOR
- IACV
- CKP SENSOR
- SENSOR UNIT:
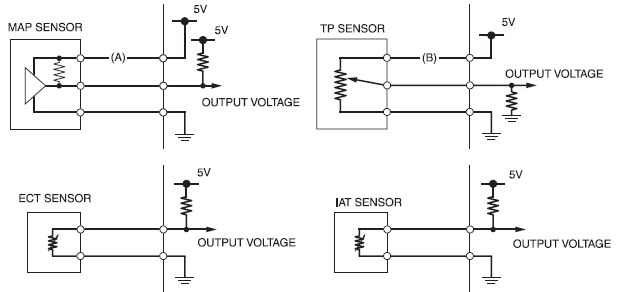
- MAP SENSOR
- IAT SENSOR
- TP SENSOR
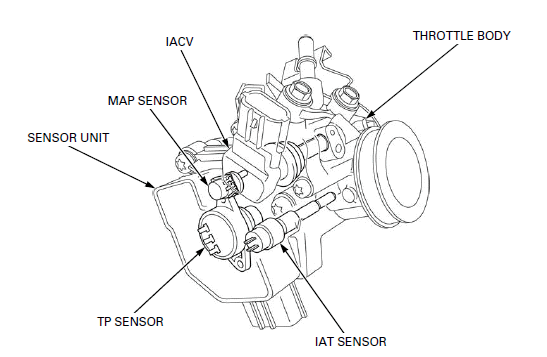
- THROTTLE BODY
- IAT SENSOR
- TP SENSOR
- SENSOR UNIT
- MAP SENSOR
- IACV
PGM-FI SYSTEM DIAGRAM
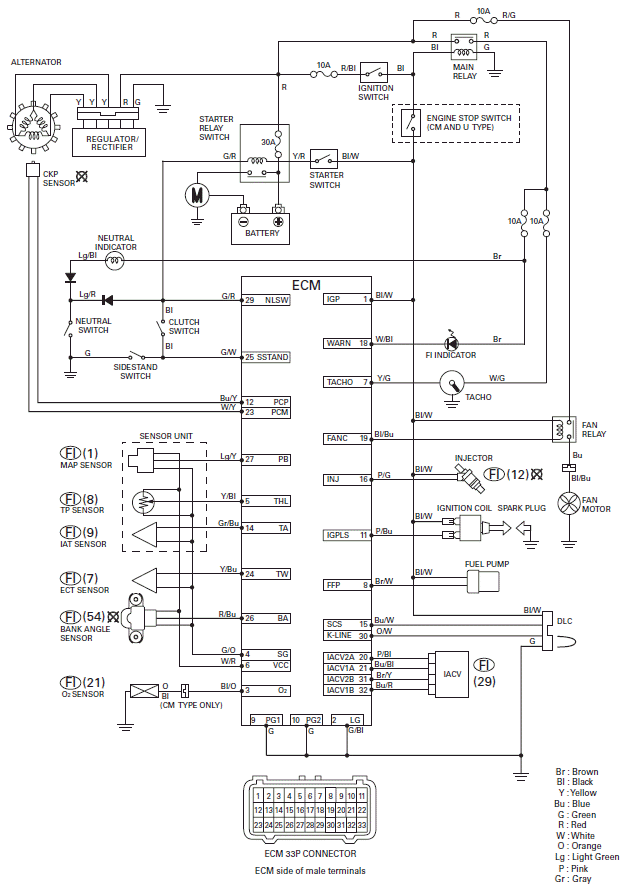
PGM-FI CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
NOTE 1: Remove the upper cowl.
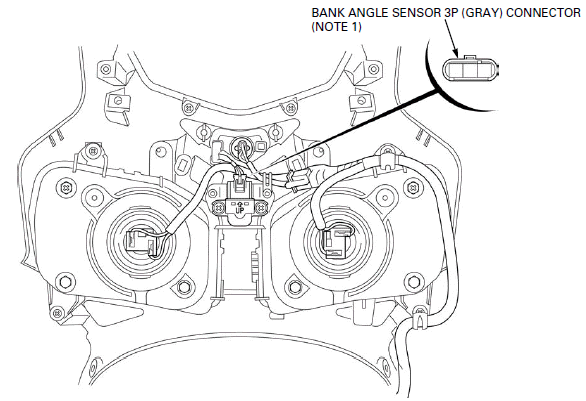
NOTE 2: Remove the right middle cowl.
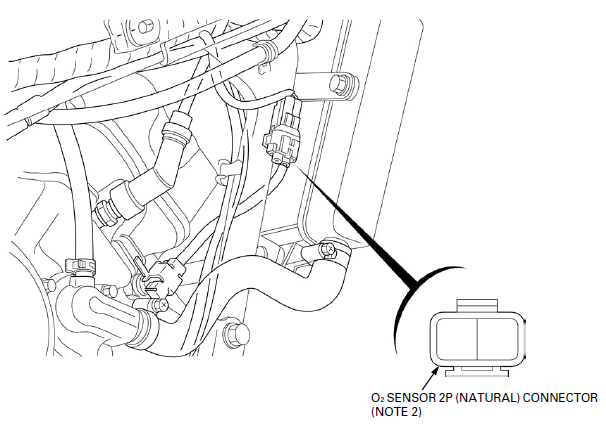
NOTE 1: Lift and support the fuel tank.
NOTE 2: Open the rubber sheet.
PGM-FI TROUBLESHOOTING INFORMATION
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING
Intermittent Failure
The term "intermittent failure" means a system may have had a failure, but it checks OK now. If the MIL does not come on, check for poor contact or loose pins at all connectors related to the circuit that of the troubleshooting. If the MIL was on, but then went out, the original problem may be intermittent.
Opens and Shorts
"Opens" and "Shorts" are common electrical terms. An open is a break in a wire or at a connection. A short is an accidental connection of a wire to ground or to another wire. In simple electronics, this usually means something will not work at all.
With ECMs this can something mean something work, but not the way it's supposed to.
If the MIL has come on
Refer to DTC READOUT.
If the MIL did not stay on
If the MIL did not stay on, but there is a driveability problem, do the SYMPTOM TROUBLESHOOTING.
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
SELF-DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
The PGM-FI system is equipped with the self-diagnostic system. When any abnormality occurs in the system, the ECM turns on the MIL and stores a DTC in its erasable memory.
FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION
The PGM-FI system is provided with a fail-safe function to secure a minimum running capability even when there is trouble in the system. When any abnormality is detected by the self-diagnosis function, running capability is maintained by pre-programmed value in the simulated program map. When any abnormality is detected in the injector, the fail-safe function stops the engine to protect it from damage.
DTC
- The DTC is composed of a main code and a sub code and it is displayed as
a hyphenated number when retrieved from the ECM with the HDS pocket tester.
The digits in front of the hyphen are the main code, they indicate the component of function failure.
The digits behind the hyphen are the sub code, they detail the specific symptom of the component or function failure.
For example, in the case of the TP sensor:
- DTC 08 - 1 = (TP sensor voltage) - (lower than the specified value)
- DTC 08 - 2 = (TP sensor voltage) - (higher than the specified value)
- The MAP, ECT, TP and IAT sensor diagnosis will be made according to the
voltage output of the affected sensor.
If a failure occurs, the ECM determines the Function Failure, compares the sensor voltage output to the standard value, and then outputs the corresponding DTC to the HDS pocket tester.
For example:
- If the input voltage line (A) on the MAP sensor is opened, the ECM detects the output voltage is about 5 V, then the DTC 1-2 (MAP sensor circuit high voltage) will be displayed.
- If the input voltage line (B) on the TP sensor is opened, the ECM detects the output voltage is 0 V, then the DTC 8-1 (TP sensor circuit low voltage) will be displayed.
MIL Blink Pattern
- If the HDS pocket tester is not available, DTC can be read from the ECM memory by the MIL blink pattern.
- The number of MIL blinks is the equivalent the main code of the DTC (the sub code cannot be displayed by the MIL).
- The MIL will blink the current DTC, in case the ECM detects the problem
at present, when the ignition switch ON (and engine stop switch "
 ":
CM and U type) or idling with the sidestand down. The MIL will stay ON when
the engine speed is over 5,000 min-1 (rpm) or with the sidestand up.
":
CM and U type) or idling with the sidestand down. The MIL will stay ON when
the engine speed is over 5,000 min-1 (rpm) or with the sidestand up. - The MIL has two types of blinks, a long blink and short blink. The long blinking lasts for 1.3 seconds, the short blinking lasts for 0.5 seconds. One long blink is the equivalent of ten short blinks. For example, when two long blinks are followed by five short blinks, the MIL is 25 (two long blinks = 20 blinks, plus five short blinks).
- When the ECM stores more than one DTC, the MIL will indicate them by blinking in the order from the lowest number to highest number.
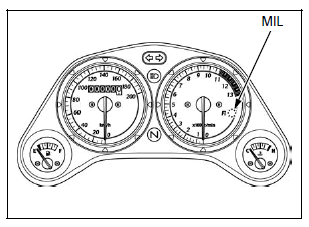
MIL Check
When the ignition switch is turned ON (and engine stop switch " ":
CM and U type) the MIL will stay on for a few seconds, then go off. If the MIL
does not come on, troubleshoot the MIL circuit.
":
CM and U type) the MIL will stay on for a few seconds, then go off. If the MIL
does not come on, troubleshoot the MIL circuit.
CURRENT DTC/FREEZE DTC
The DTC is indicated in two ways according to the failure status.
- In case the ECM detects the problem at present, the MIL will come on and the MIL will start to blink as its DTC when the sidestand is lowered. It is possible to readout the MIL blink pattern as the current DTC.
- In case the ECM does not detect any problem at present but has a problem stored in its memory, the MIL will not light and blink. If it is necessary to retrieve the past problem, readout the freeze DTC by following the DTC readout procedure.
HDS POCKET TESTER INFORMATION
- The HDS pocket tester can readout the DTC, freeze data, current data and other ECM condition.
How to connect the HDS pocket tester
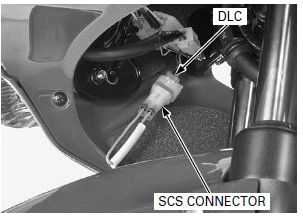
Turn the ignition switch OFF.
Remove the dummy connector from the DLC.
Connect the HDS pocket tester to the DLC.
Turn the ignition switch ON (and engine stop switch " ":
CM and U type) check the DTC and freeze data.
":
CM and U type) check the DTC and freeze data.
NOTE:
Freeze data indicates the engine conditions when the first malfunction was detected.
ECM reset
The HDS pocket tester can reset the ECM data including the DTC, freeze data and some learning memory.
After the ECM reset, follow the idle learn procedure from ECM initialization.
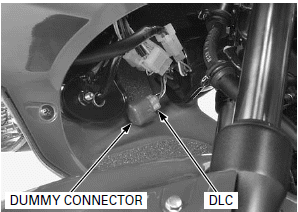
DTC READOUT
Start the engine and check the MIL.
- If the engine will not start, turn the starter motor for more than 10 seconds and check that the MIL blinks.
- When the ignition switch is turned ON (and engine stop switch "
 ":
CM and U type), the MIL will stay on for a few seconds, then go off.
":
CM and U type), the MIL will stay on for a few seconds, then go off.
If the MIL stays on or blinks, connect the HDS pocket tester to the DLC, read the DTC, freeze data and follow the troubleshooting index.
To read the DTC with the MIL blinking, refer to the following procedure.
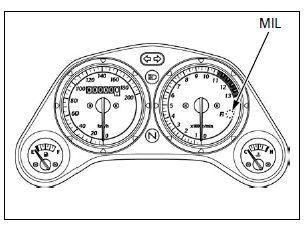
Reading DTC with the MIL
Turn the ignition switch OFF.
Remove the dummy connector from the DLC.
Short the DLC terminals using a special tool.
TOOL: SCS connector 070PZ-ZY30100
Connection: Blue/white - Green
Turn the ignition switch ON (and engine stop switch " ":
CM and U type), read, note the MIL blinks and refer to the troubleshooting
index.
":
CM and U type), read, note the MIL blinks and refer to the troubleshooting
index.
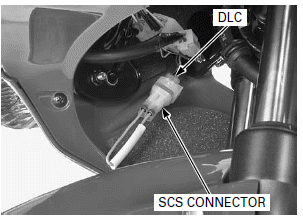
NOTE:
If the ECM has any DTC in its memory, the MIL will start blinking.
CLEARING DTC
Connect the HDS pocket tester to the DLC.
Clear the DTC with the HDS pocket tester while the engine is stopped.
To clear the DTC without HDS pocket tester, refer to the following procedure.
How to clear the DTC with SCS connector
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. Remove the dummy connector from the DLC.
Short the DLC terminals using a special tool.
TOOL: SCS connector 070PZ-ZY30100
Connection: Blue/white - Green
3. Turn the ignition switch ON (and engine stop switch " ":
CM and U type).
":
CM and U type).
4. Remove the special tool from the DLC.
5. The MIL will light for approximately 5 seconds. While the MIL lights, short the DLC terminals again with a special tool. The self-diagnostic memory is erased if the malfunction indicator goes off and starts blinking.
NOTE:
- The DLC must be jumped while the MIL lights. If not, the MIL will not start blinking.
- Note that the self-diagnostic memory cannot be erased if the ignition switch is turned OFF before the MIL starts blinking.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
INSPECTION AT ECM CONNECTOR
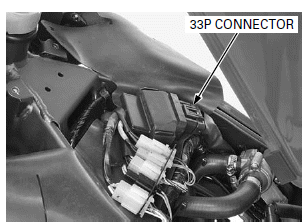
- Always clean around and keep any foreign material away from the ECM 33P connector before disconnecting it.
- A faulty PGM-FI system is often related to poorly connected or corroded terminals. Check those connections before proceeding.
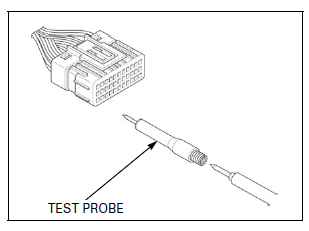
- In testing at ECM 33P connector (wire harness side) terminal, always use the test probe. Insert the test probe into the connector terminal, then attach the digital multimeter probe to the test probe.
TOOL: Test probe 07ZAJ-RDJA110
TEST HARNESS CONNECTION
Lift and support the fuel tank.
Open the rubber sheet.
Turn the ignition switch OFF.
Disconnect the ECM 33P connector.
Connect the ECM test harness between the main wire harness and ECM.
TOOL: ECM test harness 33P 070MZ-MCA0100
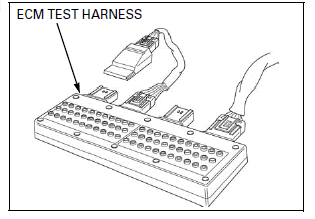
TEST HARNESS TERMINAL LAYOUT
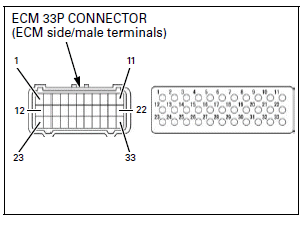
The ECM 33P connector terminals are numbered as shown in this illustration.
The ECM test harness terminals are same layout as for the ECM 33P connector terminals as shown.
See also:
 Honda CBR125RW - Service manual > Fuel System (PGM-FI)
Honda CBR125RW - Service manual > Fuel System (PGM-FI)
COMPONENT LOCATION SERVICE INFORMATION
 Honda CBR125RW - Service manual > DTC Index
Honda CBR125RW - Service manual > DTC Index
SENSOR UNIT POWER LINE INSPECTION BEFORE DTC TROUBLESHOOTING When the DTC displays 1-1, 1-2, 8-1, 8-2, 9-1 and 9-2, check the following before DTC troubleshooting. Before starting the inspection, check for loose or poor contact on the sensor unit 5P connector and ECM 33P connector.

 BMW G310GS
BMW G310GS Honda CBR125RW
Honda CBR125RW Husqvarna 401 Vitpilen
Husqvarna 401 Vitpilen KTM 890 Duke R
KTM 890 Duke R Mash Dirt Track 650
Mash Dirt Track 650 Peugeot Kisbee
Peugeot Kisbee Yamaha Tracer MT-09
Yamaha Tracer MT-09 Honda CBR125RW
Honda CBR125RW Peugeot Kisbee
Peugeot Kisbee Yamaha Tracer MT-09
Yamaha Tracer MT-09